Startup Failure Rate Statistics and Facts
Updated · Jan 31, 2025

Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Editor’s Choice
- Most Expensive Startup Failure Worldwide
- Top Reasons Startups Fail
- Startup Failure By Industry
- By Worldwide Vs Silicon Valley Startups
- Startup Failure Rates
- Startup Cost Statistics
- Scaling And Inconsistency In Startups Insights
- Startup Failure Rates In Different Countries
- Startup Failure Rate By Sector
- Startup Failure And Success Rates
- Conclusion
Introduction
Startup Failure Rate Statistics: Launching a new business can be both exciting and promising, but it also comes with its share of ups and downs. Understanding the reasons behind startup failures can help aspiring entrepreneurs navigate challenges more effectively. By analyzing data on these failures, entrepreneurs can develop strategies to mitigate risks and create adaptable business plans that increase their chances of success.
This article presents statistics on startup failures, highlighting what potential new businesses may encounter and how to prepare for these challenges. Being informed, developing a clear strategy, and stepping out with confidence are essential for overcoming obstacles in the entrepreneurial journey.
Editor’s Choice
- 90% of startups globally fail.
- 75% of US startups fold within the first 15 years.
- 20% of startups fail within the first two years, and 45% fail within the first five years.
- By the 10th year, 65% of startups have shut down.
- Industries with the highest collapse rates by the fourth year include:
- Information: 63%
- Transportation and utilities: 55%
- Retail: 53%
- Construction: 53%
- Manufacturing: 51%
- Startups operating at 42% of their full scale face a higher risk of failure by their fourth anniversary.
- Startups in sectors like online trade, securing businesses, accounting services, landscaping, and building can begin with an investment of up to USD 5,000.
- Healthcare providers, restaurants, and manufacturers are types of startups that require an initial investment of at least USD 100,000.
- 58% of small US companies start with an investment below the USD 25,000 threshold.
- 29% of startups fail due to the inability to generate market demand for their products or services.
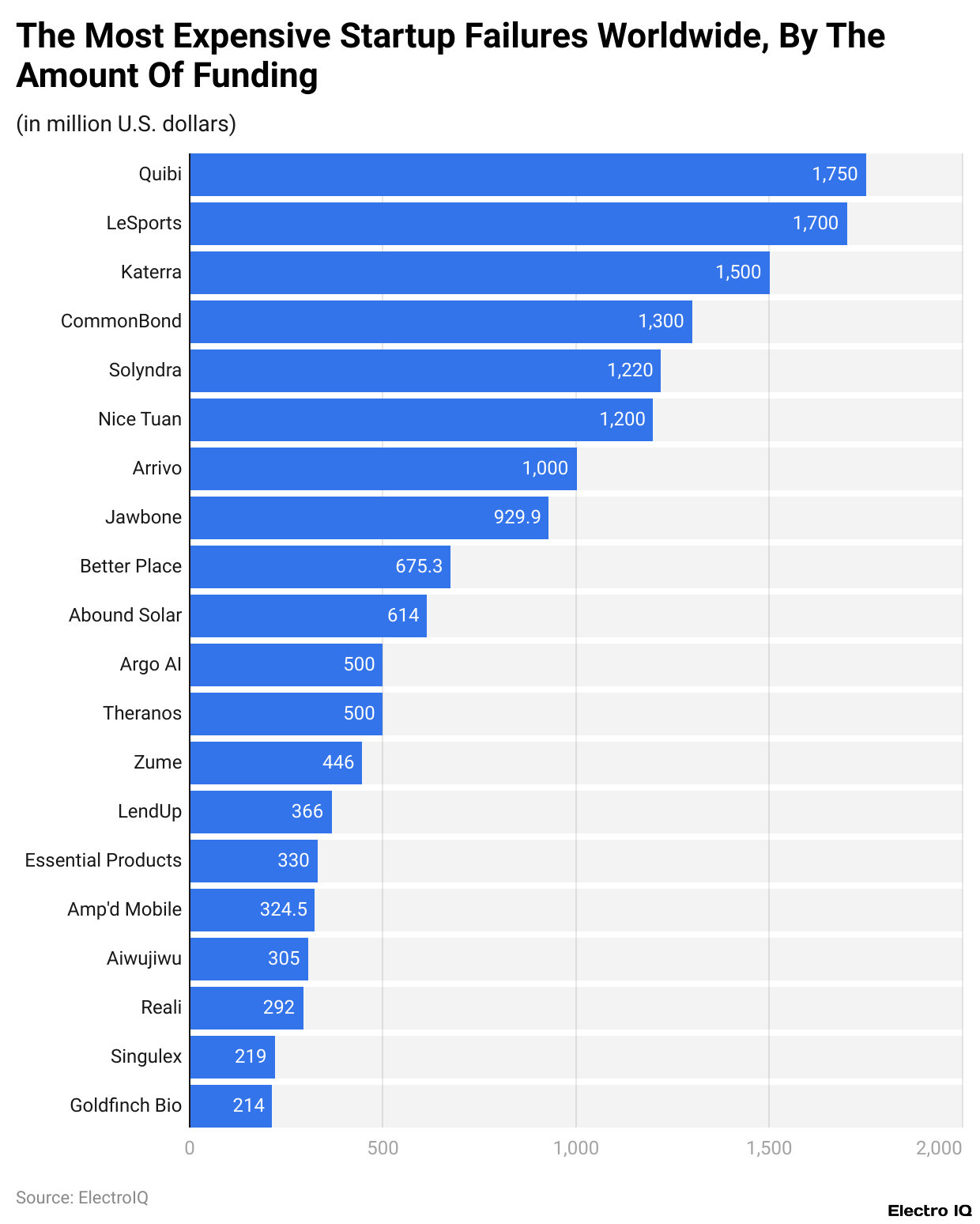
- Quibi Holdings has been announced as the most costly startup failure, with USD 1.75 billion in losses.
- In 2005, Facebook-backed investment in Quibi was USD 14.8 million, with a potential return of USD 5.6 billion or more.
- About 80% of successful startup founders indicate that a lack of funding is not the main factor for failure.
- Entrepreneurs with prior business experience have 30% higher success rates in subsequent ventures.
Most Expensive Startup Failure Worldwide
 (Reference: statista.com)
(Reference: statista.com)
- The most expensive startup failure was Quibi Holdings, which raised USD 1.75 billion in disclosed funding but shut down within six months of launching its online streaming service due to failure to capture a large enough customer base.
- The second most expensive startup failure occurred with LeEco’s Hong Kong-based streaming operation, which faced controversy with its sports competitor LeSports and incurred USD 1.7 billion in damages before closing.
- LeVision, a video streaming and production company, closed due to financial troubles despite having USD 121 million in land-based video streaming investment and USD 160 crore in funding.
Top Reasons Startups Fail
 (Reference: statista.com)
(Reference: statista.com)
- 70% of emerging tech companies do not survive, according to startup failure statistics.
- 97% of seed-crowdfunded startups fail, ending up with no success.
- Accel Partners invested USD 1 million in “thefacebook.com,” and one year later, they received a return of USD 14.8 million, a 15-fold return on their investment.
- Accel Partners invested an additional USD 77 million into Facebook.
- In 2005, Accel invested USD 14.8 million in “thefacebook.com” and received USD 5.6 billion after five years, a 378-fold return on their investment.
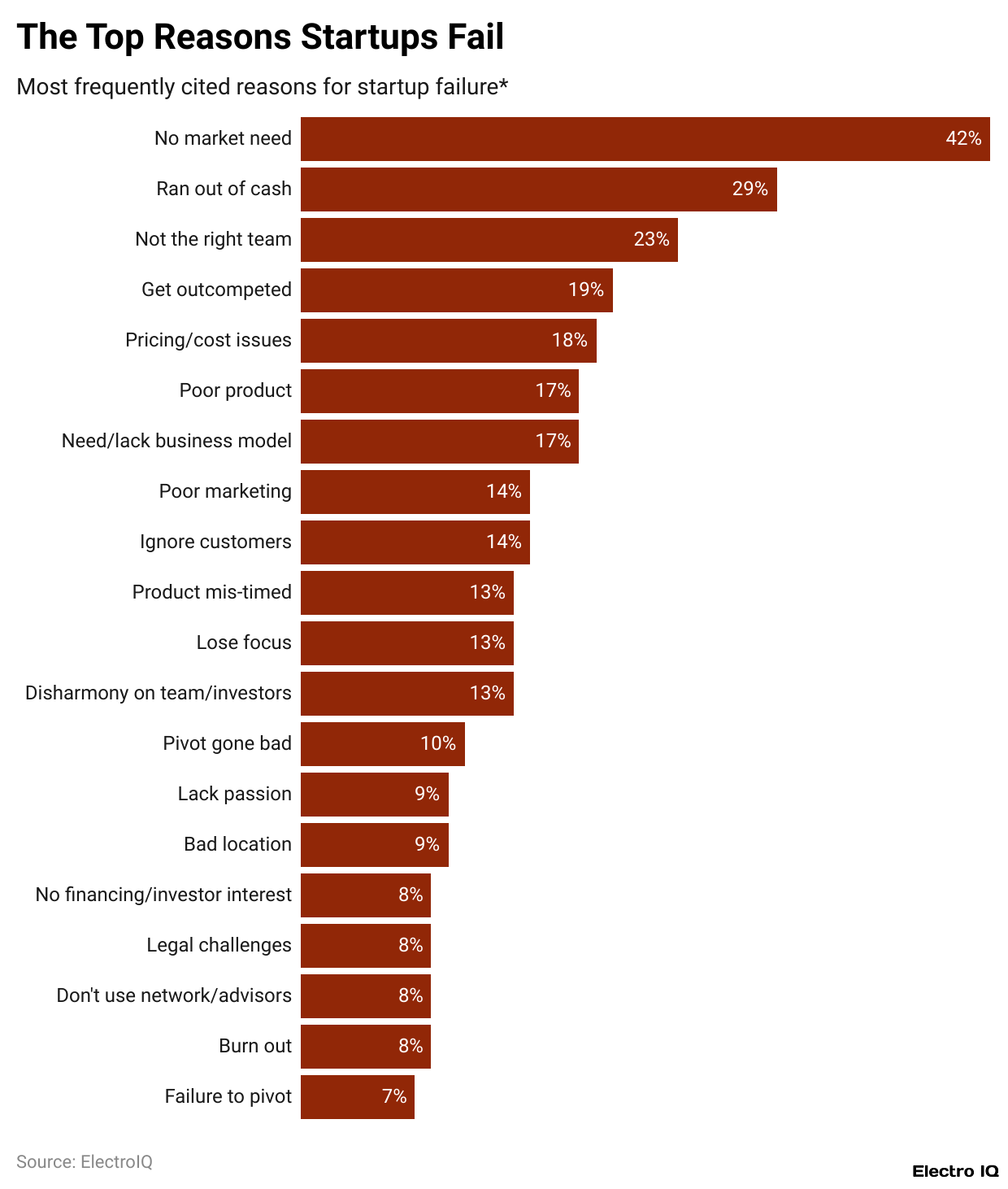
- According to CB Insights, the most common reason for startup failure is the lack of market demand for their products or services.
- 29% of startups fail due to running out of money.
- 23% of unsuccessful startups cited the lack of the right team as a primary reason for their failure.
Startup Failure By Industry
- Up to 90% of start-ups across all sectors eventually fail.
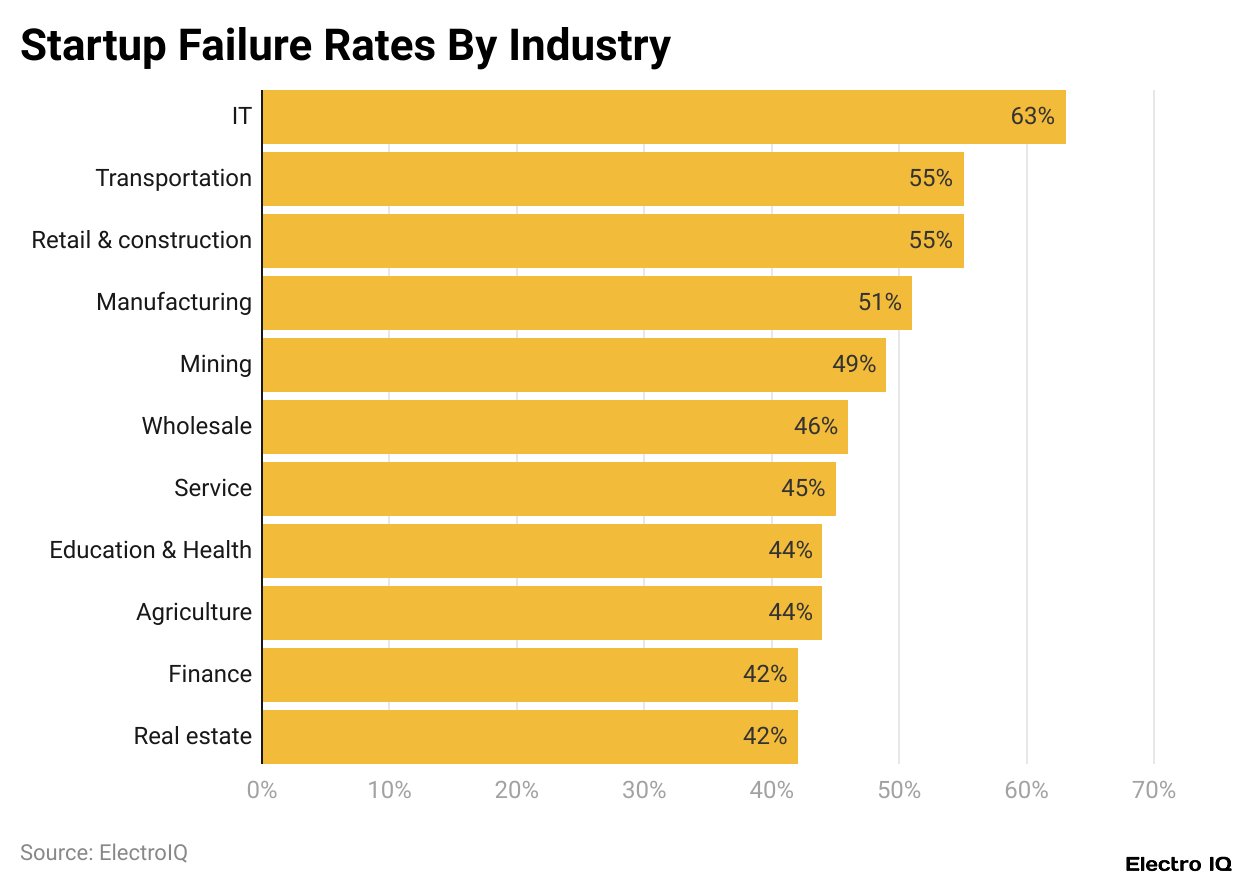
- The information industry reported the worst survival rate, with a survival probability of 63%.
- The transport and utility sector had the second-highest failure rate among start-ups at 55%.
- The failure rate for retail and construction-related start-ups was as high as 53%.
- The failure rate in the industry overall for start-ups is 51% after four years.
- Mining and wholesale sectors have a better survival rate, with failure rates of 49% and 46%, respectively.
- 45% of service start-ups fail.
- 44% of start-ups within the education, health, and agriculture sectors fail.
- Banking and real estate sectors have a lower failure rate at 42%, making them more prosperous for start-ups.
By Worldwide Vs Silicon Valley Startups
![]() (Source: startuptalky.com)
(Source: startuptalky.com)
- Startup failure statistics show in the data that the majority of startups fail internationally and also in Silicon Valley.
- The numbers could be different, but one of the studies claimed that 90% of them fail internationally, while 83 fail in Silicon Valley, bringing out the immediate similarity: Startups hardly succeed.
- Thus, such incidents are indicative of the risks that come with setting up new businesses in any part of the world.
Startup Failure Rates
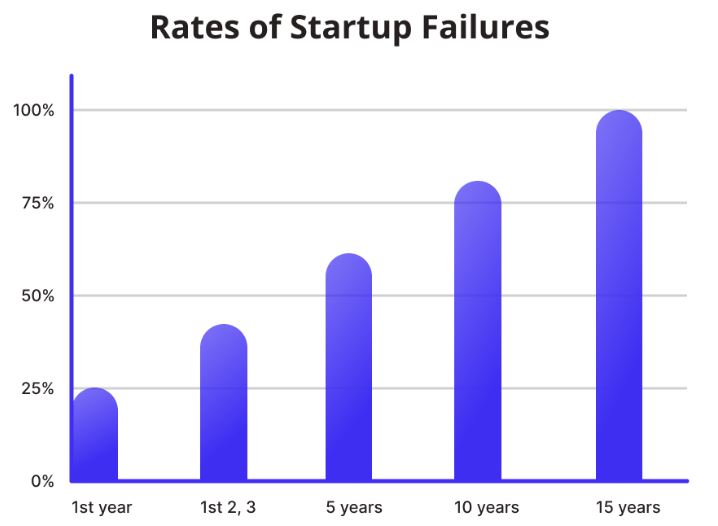 (Source: victorflow.com)
(Source: victorflow.com)
- The rate of business discontinuation in the United States is brought out by the incidence data of the Bureau of Labor Statistics, which directly specifies that many startups fail during their initial years.
- For example, about 20% never pass the operational growth phase when they are not yet two years old, and 45% give up before reaching their fifth birthday.
- In a longer context, 65% would have exited business before a decade, and 75% fail even in as short as 15 years while operating in the United States.
- These numbers illuminate the same obstacles new businesses suffer and characterize the insights in failing. Through a detailed check of these trends, entrepreneurs will come to learn meaningful reopening strategies.
Startup Cost Statistics
- Startup failure statistics indicate that the costs of startups can vary greatly depending on the industry at hand. E-commerce, accounting, landscaping, and construction will require less than USD 5,000 to start work.
- However, healthcare, restaurants, or manufacturers would all need over USD 100,000 in initial investment.
- Also, equipment costs range from USD 10,000 to over USD 125,000 on the high-end, depending much on the equipment being used and the kind of field a business is in.
- The bulk of costs will come in the form of payroll, with the average startup cost for five employees in the U.S. being USD 300,500.
- The majority (58%) of small U.S. businesses would start with less than USD 25,000 in funding.
- However, some sectors in America, especially those that are backed through venture capital, such as ride-hailing services and short-term rentals, require billions in debt to become successful.
- Especially with healthcare, startups have to spend a lot of money. The start-up costs would be largely dependent upon where the start-up is located.
- To illustrate, New York City has some of the costliest office space, at an average of USD 68 per square foot per month. In contrast with Detroit, cheap office space is at USD 16 per square foot every month.
- Detroit, however, has limited remote location options along with some of the highest internet service costs.
Scaling And Inconsistency In Startups Insights
- The Startup Genome Project identifies the stages of transforming a startup into a business: Discovery, Validation, Efficiency Scaling & Scale.
- However, the impact of scaling prematurely on future success is much greater in those later stages.
- Startup failure statistics state that during the Efficiency stage, they become more generous (three times more) with capital, but less outlay for Scaling (18 times less). Inconsistent startups have higher pre-scale valuations (USD 10M) than consistent ones (USD 800K).
- In the primary stages, accelerated startups tend to onboard even more paid users (75% difference), while there is an increasing number of paid users for already established startups in the Growth phase (50%).
- Accelerated startups code significantly more at an early stage (3.5 times in Discovery and 2.25 times in Efficiency), thereby suggesting that the funding and concentration of productions are inappropriate.
Startup Failure Rates In Different Countries
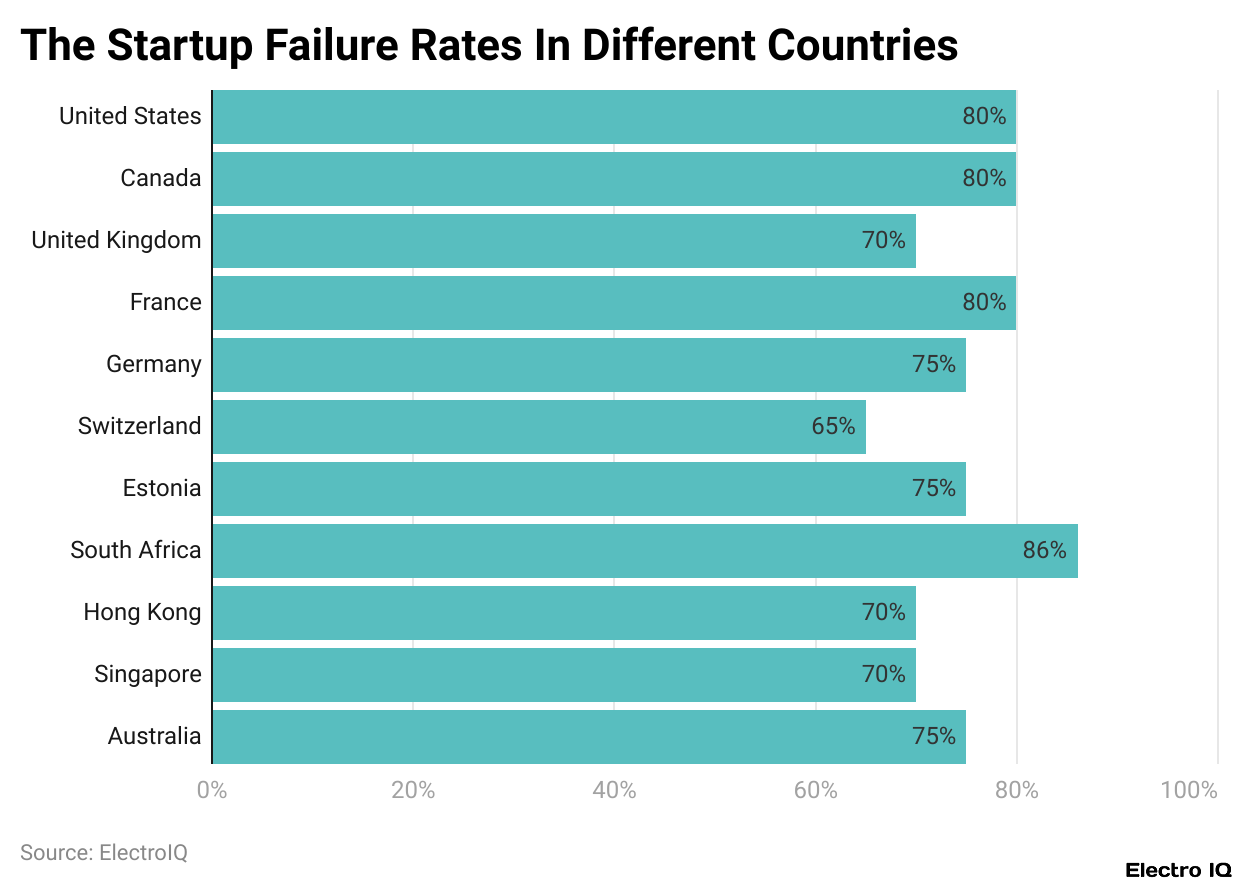
- According to startup failure statistics, failure rates of entrepreneurship are at a very high level across every country countries’ rates are very high. The rate here is from 65% in Switzerland to 86% in South Africa.
- There are most of the United States, Canada, France, and Germany, all at an 80% rate.
- The United Kingdom, Hong Kong, and Singapore all reside at a failure rate of 70% which is very slightly lower than the failure rate of 75% shown by the Republic of Estonia and Australia.
- It is clear to note that starting a business across the globe presents a health risk in both rich and poor countries.
- Since most start-ups in any country are highly vulnerable to death, if a few cross over it might be just easy for some and almost impossible for some when one identifies a small difference among countries.
Startup Failure Rate By Sector
- Fintech is the future, leveraging technology and innovation to challenge traditional finance structures.
- Startup failure statistics state that while they have a lower rate of failure than most industries, roughly three-quarters of them will fail. The growth seen by fintechs is incredible: from a global investment of USD 1.8 billion in 2011, it has grown to a whopping USD 30.8 billion in 2018.
- The industry actually amounted to quite USD 310 billion in value by 2022, with the United States alone profiling over 8,775 fintech startups.
- The technology startup ecosystem is dotted with corporate giants like Facebook, Apple, and Google, and there is super fierce competition among the corporations.
- Nevertheless, this sector is very difficult, with almost one out of every three failing in the first five years. Notwithstanding this, 20 can generate USD 100 million in revenue from the 100 tech companies launched in the US.
- The average age of an American tech founder is 39 years, and technology-related data centres typically pay their employees USD 102,000 annually.
- Real estate startups have a higher rate of failure than any other dynamic sector in the US – an expected 48% are headed for collapse in the next four years – but they are very much on the table for 31% of US commercial vs property investors.
- US-based commercial investors want in on Proptech. The industry’s revenue retained USD 1.9 billion for the year 2019 in the USA.
Startup Failure And Success Rates
- It is important because the founders of successful start-ups, on average about 80%, believe that while a small follow-up fund is sufficient, the root attributes of their success lie in their expertise and experience.
- This clearly indicates that while capital is very important, firm leadership and skilful members of the team are equally important, and neglect of these foundational elements causes many firms to miss obtaining funds minding only finance.
- As evidenced, healthcare has seen start-ups produce substantial revenue in the US alone as of 2017, along with other sectors of the economy.
- The industry has seen a hike with an aggregate revenue of USD 36.3 billion. One reason for this increase is the increased integration of technology into the health sector.
- 24% of the reasons companies say they fail at a later stage of their start-up journey are to be connected to these attributes.
- Now it is customer neglect that makes up 14% of cases of failure. Ignoring customer needs can stall growth badly because they generally focus on product development, marketing, and fine-tuning their business model.
- Companies that feel they are successful often lose customers to competitors when they don’t fully understand customer frustration levels.
- The mining industry shows a surprising 51.3 five-year survival rate, one of the highest rates among several sectors and not without unique challenges and opportunities within the industry.
- There is a vast pool of start-up failures, with 90% of them failing in general.
- The figures underline the high risk that business start-ups take, with 70% not making it through to the end of the second or fifth year and 10% calling it quits during the first year.
- Competition particularly plays a significant role in start-ups, especially for those start-ups in their third to fifth year.
- The market increasingly becomes full of new entrances and new business models, competition heats up-making market share maintenance for existing businesses quite a challenge.
- The lack of capital for their enterprise has been a significant obstacle for those budding entrepreneurs, as identified by 29% of them as the second most significant reason for failure. Insufficient funds often result in long-time borrowing, leading to financial strain on the enterprise.
- A strong team makes for success; 23% of failures among start-ups can be attributed to the lack of a competent team and 19% due to their being out-competed by rivals.
- Creating a strong, cohesive team with diverse competencies and expertise will be vital in these areas and will help overcome the disaster in competitive markets.
- Rates of failure generally seem constant in the industry; the sort of business, the business model, the entrepreneurial team, and, access to funding are the elements that determine success or failure.
- 82% realized that financial problems have become a significant killer of business, with approximately 82% of businesses closing in 2018 because of the same issues.
- Good financial management will be something you should have allowing your company to have enough capital to support it.
- Even though around 80% of small businesses go through their first year, only 30% of start-up companies will advance into ten-year-old businesses.
- However, the future suggests a less optimistic outcome, with only 70% entering the second year, and most only making it to the end of a five-year period.
- There is a 30% higher chance of success in their subsequent endeavours with the entrepreneurs who have already had prior business experience.
Conclusion
Startup failure statistics have shown that by 2025, startup failures will be global evidence that one should always think ahead and operate soon enough in the market’s demand loop. With such sure opportunities, one should not fear launching a start-up simply because the risk is unavoidable in start-ups.
This means lessons can be learned from past mistakes and an approach adopted that is heavily data-driven to achieve robust businesses. Future of startup ecosystem: The ecosystem is likely to bring more challenges to the themes and trends in the business environment.
Sources
FAQ.
The highest reason leading to the failure of a start-up company can be traced to a lack of market demand as far as its product or service is concerned (29% of the failures stated in the aforementioned study). This is the very reason why you will vigorously perform research related to market applications before putting up one.
Usually, about 90% of startup businesses fail worldwide, with a good 75% failure rate within their first 15 years in the US as well.
The last few explanations can be seen in the following: Lack of market demand for the product or service offered (29%) and running out of money (29%). Actually having weak or unsuitable team setup (23%), Very heavy competition (19%): Customer neglect (14%)
Within just four years, the information industry records the highest 63% of failed startups, and this is followed by transportation and utilities (both with 55%). The %age of retail and construction also appears in an ample ratio i.e. 53%. A high %ages of failed start-ups is also reported from the remanufacturing industry which has a 51% loss.
Conduct thorough market research to ensure that there is demand for your product or service. Set up a very sound team with better skills and experience to bring success. Ensure secured financing for the initial operational expenses and costs. Implement a sound financial management plan to track revenue and expenses. Give more priority to customer satisfaction plus fantastic customer service. Move and innovate continuously to stay well ahead of the competitors.

Joseph D'Souza founded ElectroIQ in 2010 as a personal project to share his insights and experiences with tech gadgets. Over time, it has grown into a well-regarded tech blog, known for its in-depth technology trends, smartphone reviews and app-related statistics.