Train Statistics By Company, Manufacturers And Infrastructure Projects
Updated · Nov 07, 2024

Table of Contents
Introduction
Train Statistics: Rail transportation focuses on using vehicles that run on track, which consist of a parallel set of rails. It is one of most common form of transportation. It is the most common form of cargo transportation used by countries worldwide. As we go forward, we will learn about train statistics to understand this form of transportation. Accordingly, we will learn about the essential measures taken to ensure this has become an eco-friendly form of transportation, thus a means for low C02 emissions and carbon footprint.
Editor’s Choice
- CRRC Corp Ltd has the highest market share in metro rolling stock at 73%.
- The L0 series Maglev from Japan is the world’s fastest train, reaching 603 km/h.
- Union Pacific from the US has the highest market value among railway companies at $149.46 billion.
- The UK’s High Speed 2 rail link is the highest-valued rail infrastructure project at $86 billion.
- China’s railway network is the largest, spanning 159,000 km with 75.20% electrification.
- India has the highest percentage of electrified railway networks at 93.43%.
- The United States has the most extended railway network at 220,044 km, but only 0.84% is electrified.
- Belgium has the highest density of electrified railways per route km at 8.48.
- The global high-speed rail market was valued at approximately $350 billion in 2023.
- China accounts for about 45% of the global train market.
- The California High-Speed Rail project in the US is valued at $80.3 billion.
- The Trans-European Network is valued at $67 billion, a 5% increase from 2023.
- Railway infrastructure investments are expected to grow by 8% annually in 2024.
- The US had the most extended historical peak railway length at 428,180 km in 1917.
- Japan’s railway network is 75.19% electrified, among the highest percentages globally.
Leading Metro Rolling Stock Manufacturers
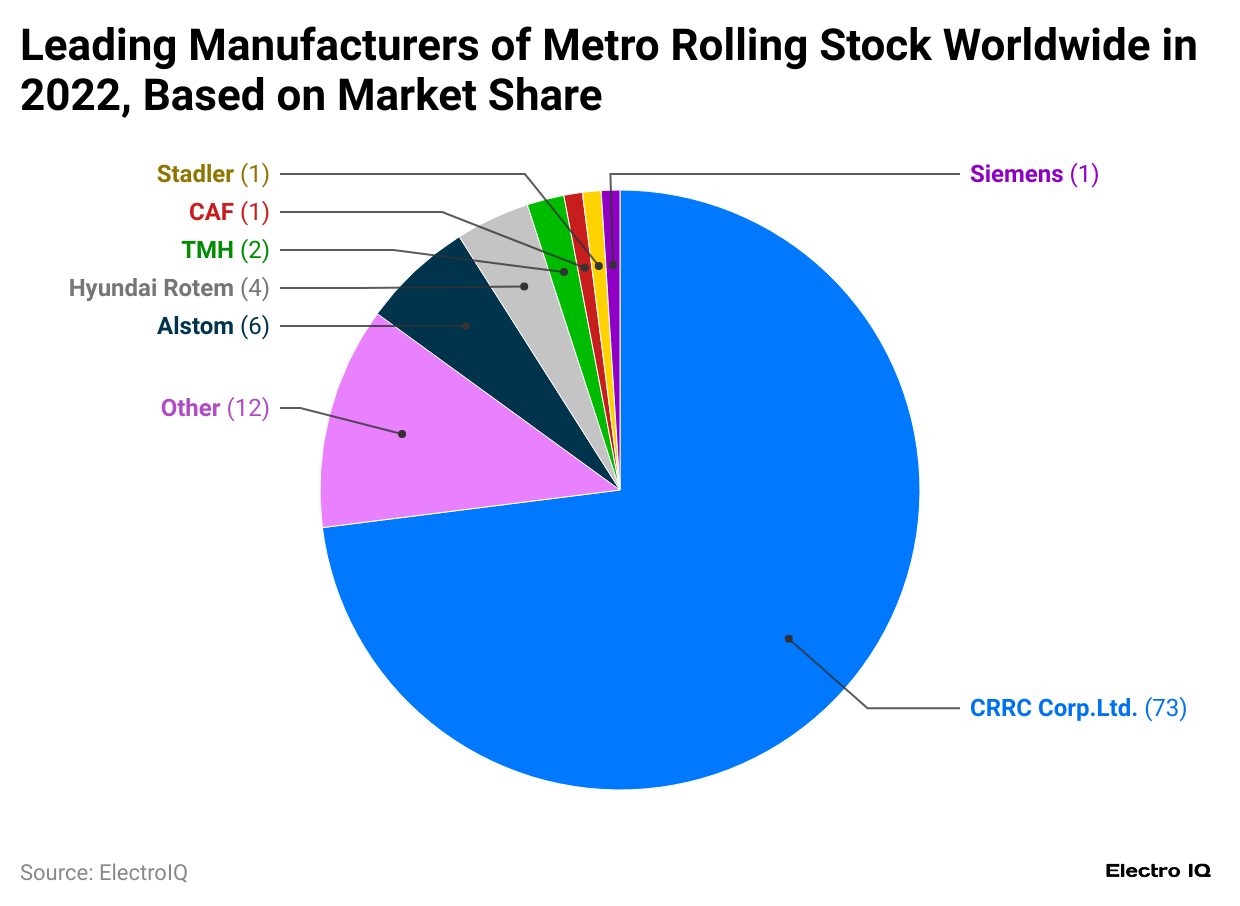
(Reference: statista.com)
- Train Statistics show that Alstom, Siemens, Stadler, Hyundai Rotem, CAF, CRRC Corp. Ltd., TMH, and others are top manufacturers of metro rolling stock.
- BRBC Corp Ltd has highest market share with 73% followed by Other companies with 12%, Alstom with 6%, Hyundai Rotem with 4%, TMH with 2%, Stadler with 1%, Siemens with 1%, CAF with 1%.
Fastest Train in World
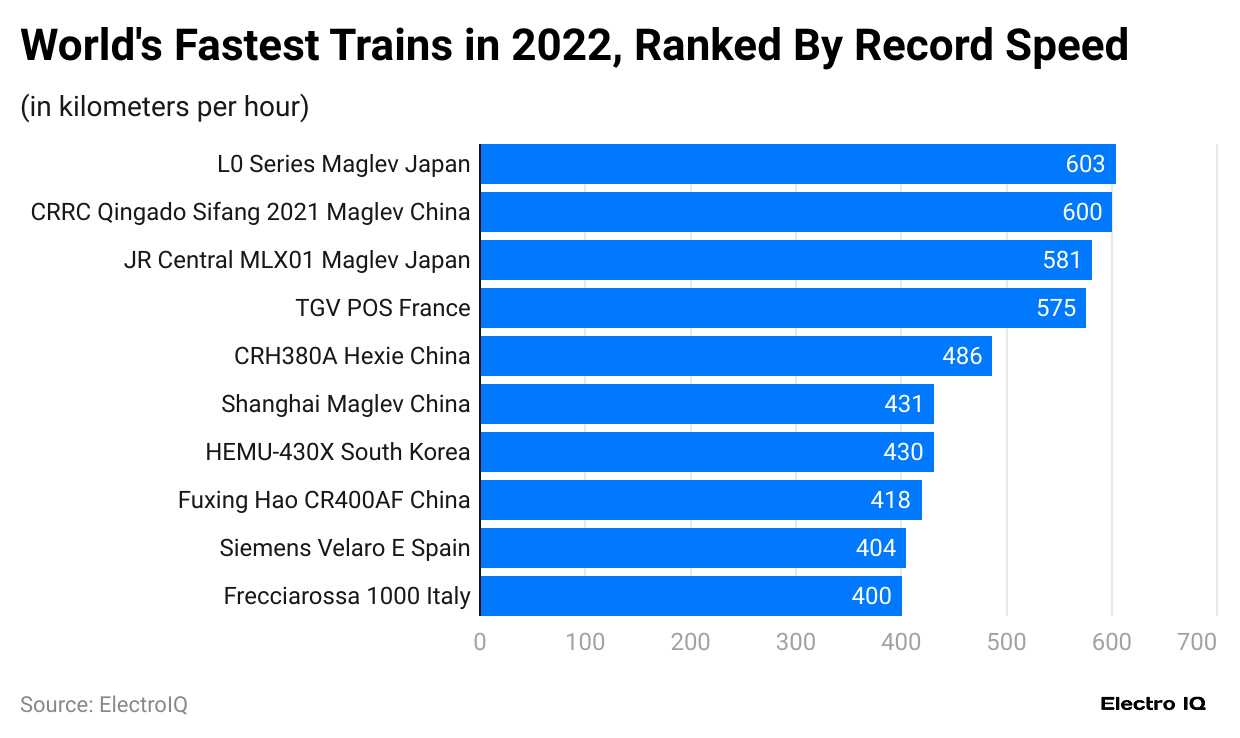
(Reference: statista.com)
- Train Statistics show that CRRC from China, JR Central from Japan, TGV from France, CRH from China, Siemens from Spain, Shanghai Maglev from China, HEMU from South Korea, Fuxing Hao from China, and Frecciarossa from Italy rank among the world’s fastest trains.
- LO series Maglev from Japan is the fastest, with 603 km/h, followed by L0 Series from Japan with 603 km/h, CRRC Qingdao Sifang from China with 600 km/h, JR Central from Japan with 581 km/h, TGV from France with 575 km/h, CRH from China with 486 km/h, Shanghai Maglev from China with 431 km/h, HEMU from South Korea with 430 km/h, Fuxing Hao from China with 418 km/h, Siemens from Spain with 404 km/h, Frecciarossa from Italy with 400 km/h top speed.
World’s Largest Railway Company
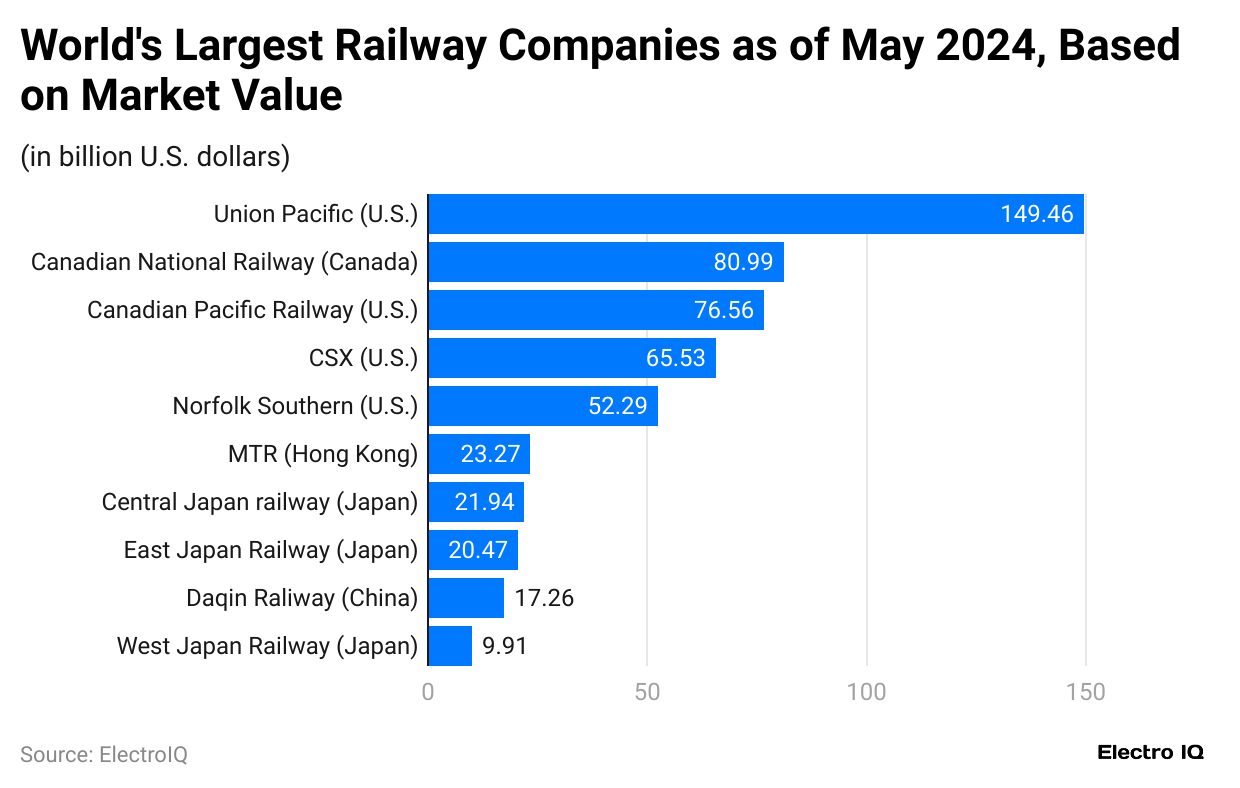
(Reference: statista.com)
- Train Statistics show that MTR from Hong Kong, Union Pacific from the U.S., Canadian National Railway from Canada, West Japan Railway from Japan, CSX from the U.S., Daqin Railway from China, Norfolk Southern from the U.S., East Japan Railway from Japan, Central Japan Railway from Japan, Canadian Pacific Railway from U.S rank among top railway companies worldwide.
- Union Pacific from the US has the highest market value with $149.46 billion, followed by Canadian National Railway from Canada with $80.99 billion, Canadian Pacific Railway from U.S. with $76.56 billion, CSX from U.S. with $65.53 billion, Norfolk Southern from U.S. with $52.29 billion, MTR from Hong Kong with $23.27 billion, Central Japan Railway from Japan with $21.94 billion, East Japan Railway from Japan with $20.47 billion, Daqin Railway from China with $17.26 billion, West Japan Railway from Japan with $9.91 billion.
Largest Rail Infrastructure Projects
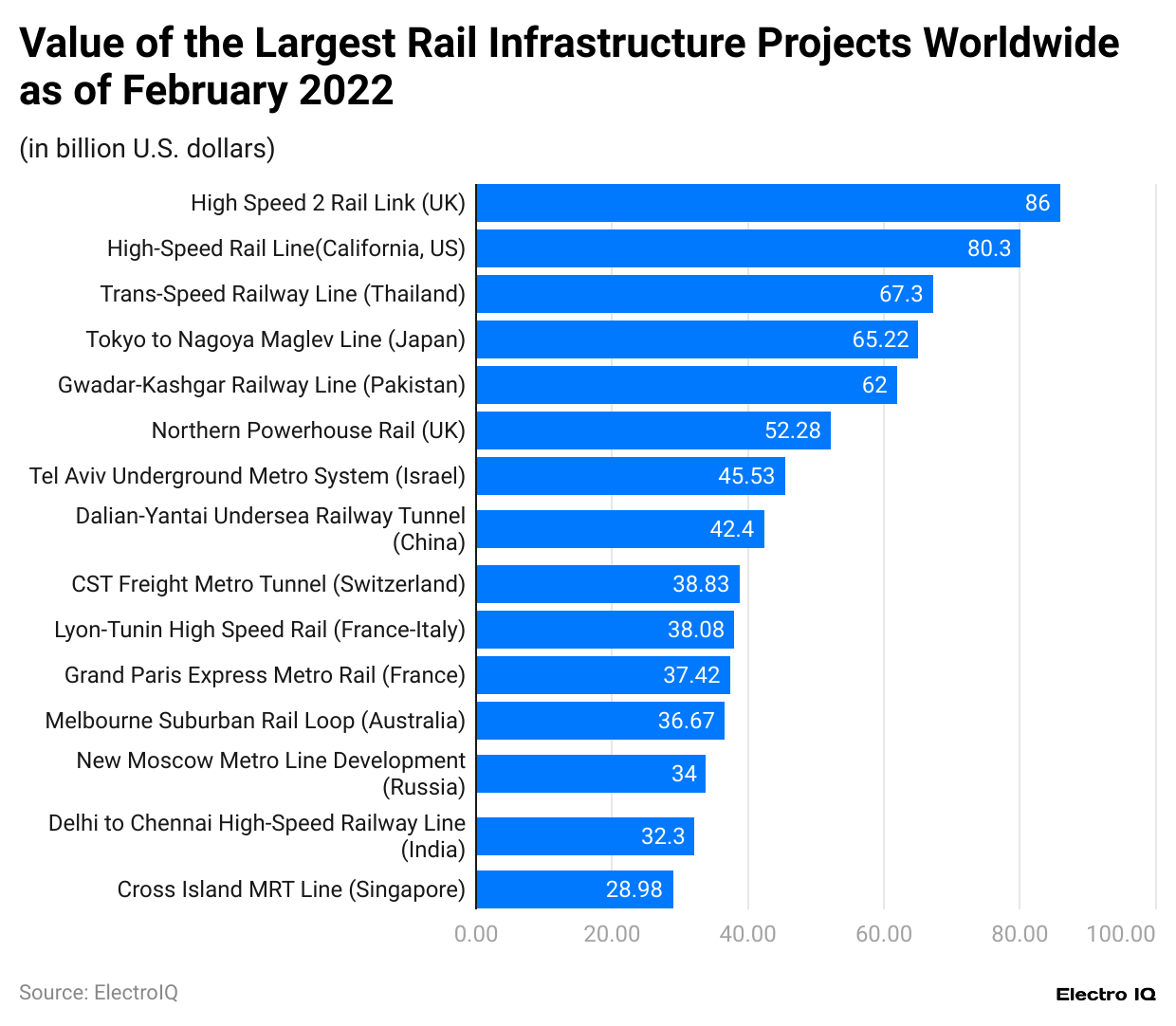
(Reference: statista.com)
- Train Statistics show that the Grand Paris Express Metro Rail from France, the Gwadar-Kashgar Railway Line from Pakistan, the High-Speed Rail Line from US, Cross Island MRT Line from Singapore, the Tokyo to Nagoya Maglev Line from Japan, CST Freight Metro Tunnel from Switzerland, High Speed 2 Rail Link from UK, Tel Aviv Underground Metro System from Israel, Lyon-Turin High-Speed Rail from France-Italy, Dalian-Yantai Undersea Railway Tunnel from China, Trans-Asean Railway Line from Thailand, Northern Powerhouse Rail from UK, Melbourne Suburban Rail Loop from Australia, New Moscow Metro Line Development from Russia, Delhi to Chennai High-Speed Railway Line from India rank among highest valued projects worldwide.
- High speed 2 rail link from the UK has the highest rail infrastructure value with $ 86 billion, followed by High-Speed Rail Line from US with $80.3 billion, Trans-Asean Railway Line from Thailand with $67.3 billion, Tokyo to Nagoya Maglev Line from Japan with $65.22 billion, Gwadar-Kashgar Railway Line from Pakistan with $62 billion, Northern Powerhouse Rail from UK with $52.28 billion, Tel Aviv Underground Metro System from Israel with $45.53 billion, Dalian-Yantai Undersea Railway Tunnel from China with $42.4 billion, CST Freight Metro Tunnel from Switzerland with $38.83 billion, Lyon-Turin High-Speed Rail from France-Italy with $38.08 billion, Grand Paris Express Metro Rail from France with $37.42 billion, Melbourne Suburban Rail Loop from Australia with $36.67 billion, New Moscow Metro Line Development from Russia with $34 billion, Delhi to Chennai High-Speed Railway Line from India with $32.3 billion, Cross Island MRT Line from Singapore with $28.98 billion.
List of Railways Worldwide
#1. Asia
- Afghanistan: Railheads from neighboring countries planned links to Iran and Turkey.
- China: China Railway (CR), China Railway High-speed (CRH), Beijing-Shanghai High-Speed Railway Co. Ltd
- India: Indian Railways (IR), Indian Railway Catering and Tourism Corporation (IRCTC), High-Speed Rail Corporation of India Limited (HSRC), Rail Vikas Nigam Limited (RVNL), multiple urban transit systems including Kolkata Metro Rail Corporation, Delhi Metro Rail Corporation
- Indonesia: Kereta Api Indonesia (PT KAI), Jakarta MRT, Jabodebek LRT (Greater Jakarta LRT)
- Japan: Japan Railways Group (JR Group)
- South Korea: Korail, Seoul Metro, AREX, Busan Transportation Corporation
- Bangladesh: Bangladesh Railway, Dhaka Metro Rail
- Nepal: Nepal Railways
- Philippines: Philippine National Railways, Light Rail Transit Authority (Line 1 and Line 2), Metro Rail Transit Corporation (Line 3)
- Singapore: SBS Transit, SMRT Trains
- Vietnam: Vietnam Railways
- Iran: Islamic Republic of Iran Railways
- Israel: Israel Railways, Carmelit, Cfir (Jerusalem Light Rail), NTA (Tel Aviv Light Rail)
- Malaysia: Keretapi Tanah Melayu Berhad (KTMB), Prasarana Malaysia – Rapid Rail Sdn Bhd, Express Rail Link Sdn. Bhd.
- Pakistan: Pakistan Railways (PR), Karachi Circular Railway (KCR)
- Sri Lanka: Sri Lanka Railways
- Thailand: State Railway of Thailand, S.R.T. Electrified Train Company Limited, Bangkok Mass Transit System (BTSC)
- Turkmenistan: Demirýollary
#2. Latin America and the Caribbean
- Argentina: Trenes Argentinos, Ferrovías, Metrovias
- Belize: No active railway system
- Brazil: Rede Ferroviária Federal SA (RFFSA), MRS Logística, Companhia Paulista de Trens Metropolitanos (CPTM)
- Chile: Empresa de los Ferrocarriles del Estado (EFE), FEPASA, Ferronor
- Colombia: Ferrocarriles Nacionales de Colombia
- Costa Rica: Instituto Costarricense de Ferrocarriles (INCOFER)
- Cuba: Ferrocarriles Nacionales de Cuba (Cuban National Railways)
- Paraguay: Ferrocarril Presidente Carlos Antonio Lopez
- Peru: Empresa Nacional de Ferrocarriles del Peru (ENAFER)
- El Salvador: Ferrocarriles Nacionales de Salvador (FENADESAL)
- Uruguay: Administración de Ferrocarriles del Estado (AFE)
- Venezuela: Instituto Autónomo de Ferrocarriles del Estado (IAFE)
#3. Oceania
- Australia: Pacific National, Aurizon, V/Line, Queensland Rail
- New Zealand: KiwiRail, Auckland One Rail, Dunedin Railways
#4. North America
- Canada: Canadian National Railway, Via Rail, GO Transit, Rocky Mountaineer
- Mexico: Ferrocarriles Nacionales de Mexico (FNM), Ferromex, Kansas City Southern de México (KCSM)
- United States: Amtrak, Union Pacific Railroad, BNSF Railway, CSX Transportation, Norfolk Southern Railway
#5. Europe
- Albania: Albanian Railways (HSH)
- Austria: ÖBB (Austrian Federal Railways)
- Azerbaijan: Azerbaijan Railways (ADY), Baku Metro
- Belgium: NMBS/SNCB (Belgian National Railways)
- Czech Republic: ČD (Czech Railways), ČDC (ČD Cargo), RegioJet, LEO Express
- Denmark: DSB (Danish State Railways), Banedanmark, Arriva Danmark
- Estonia: Eesti Raudtee (Estonian Railways)
- Finland: VR Group
- France: SNCF (French National Railways), Eurostar, Thalys, RATP
- Germany: Deutsche Bahn (DB), Regio-Bahn GmbH, S-Bahn Berlin GmbH, Harzer Schmalspurbahnen
- Greece: TrainOSE (Greek Railways Organization)
- Hungary: MÁV-START, Rail Cargo Hungaria
- Ireland: Iarnród Éireann – Irish Rail
- Italy: Ferrovie dello Stato (FS), Trenitalia, ATM (Milan Metro), Metropolitana di Roma (Rome Metro)
- Latvia: Latvian Railway (LDz)
- Lithuania: Lithuanian Railways (LTG)
- Luxembourg: CFL (Luxembourg Railways)
- Netherlands: Nederlandse Spoorwegen (NS), Arriva Netherlands, DB Cargo
- Norway: Vy, Bane NOR, CargoNet, Airport Express Train
- Poland: Koleje Mazowieckie, PKP Cargo, Polregio
- Portugal: CP (Portuguese Railways)
- Romania: CFR Călători, CFR Marfă, Metrorex (Bucharest Metro)
- Russia: RZhD (Russian Railways)
- Spain: Renfe, Adif (Railway Infrastructure Manager), EuskoTren (Basque Railways)
- Sweden: SJ (State Railways), MTR Express, Green Cargo
- Switzerland: SBB CFF FFS (Swiss Federal Railways), Rhätische Bahn, Matterhorn-Gotthard-Bahn
- Turkey: TCDD (Turkish State Railways)
- Ukraine: UZ (Ukrainian Railway)
- United Kingdom: Avanti West Coast, Great Western Railway, Eurostar
#6. Africa
- Botswana: Botswana Railways
- Mauritius: Light rail Metro Express (Mauritius)
- Togo: Togo Railways (RCFT)
- Tunisia: Tunisian National Railways (SNCFT)
- Ghana: Ghana Railways & Ports (GRP), Ghana Railway Company
- Kenya: Kenya Railways, Rift Valley Railways Consortium, Africa Star Railway Operation Company Limited
- Morocco: Office National des Chemins de Fer (ONCF)
- Egypt: Egyptian Railways
- Eritrea: Eritrean Railway
- Djibouti: Ethio-Djibouti Railways
- Benin: Benin Railways (Benirail & Bolloré Railways since 2014)
- Swaziland (Eswatini): Eswatini Railways (Swaziland Railway)
- Tanzania: Tanzania Railways Corporation, TAZARA Railway
- Namibia: TransNamib
- Zimbabwe: National Railways of Zimbabwe, Beitbridge Bulawayo Railway
- South Africa: Blue Train (Tour trains), Passenger Rail Agency of South Africa, Transnet Freight Rail, Gautrain (High-Speed Trains)
- Angola: Benguela Railway, Moçâmedes Railway, Luanda Railway, Gunza-Gabala line
- Mozambique: Caminhos de Ferro de Moçambique (Mozambique Railway), Beira Railroad Corporation
- Burkina Faso: Abidjan-Niger Railway (SITARAIL)
- Cameroon: Cameroon National Railways Authority (REGIFERCAM)
- Republic of the Congo: Congo-Ocean Railway (CFCO)
- Democratic Republic of the Congo: Congo Railway (CNC), Matadi-Kinshasa Railway
- Malawi: Malawi Railways, Central East African Railway
- Mali: Dakar-Niger Railway
- Liberia: Bong Mining Co, Lamgo JV Operating Co
- Algeria: Algerian Railways (SNTF)
- Lesotho: South African Railways (SAS/SAR)
- Senegal: Dakar-Niger Railway
(Source: wikipedia.org)
Countries By The Size of The Rail Transport Network
| Country/Territory | Length (km) | Electrified (km) | % of Total Electrified | Per Route km (Electrified) | Area (km²) | Population | Historical Peak Length (km) | Nationalized or Private | Data Year | ISO 3166-1 |
| Belgium | 3,607 | 2,960 | 82.06% | 8.48 | 3,140 | 5,081 (1940) | Nationalized | 2018 | 56 | |
| Kazakhstan | 15,530 | 4,200 | 27.04% | 175 | 1,146 | Nationalized | 2016 | 398 | ||
| Australia | 33,168 | 3,393 | 10.23% | 231.91 | 742 | Both | 2017 | 36 | ||
| Nigeria | 3,600 | 0 | 0.00% | 261.84 | 44,904 | Nationalized | 2006 | 566 | ||
| China | 159,000 | 119,000 | 75.20% | 60.61 | 8,865 | 159,000 (2023) | Nationalized | 2023 | 156 | |
| Turkey | 13,128 | 6,244 | 47.60% | 76 | 7,821 | Nationalized | 2022 | 792 | ||
| India | 68,584 | 64,080 | 93.43% | 47.93 | 21,038 | 68,584 (2023) | Nationalized | 2024 | 356 | |
| United Kingdom | 16,179 | 6,065 | 37.49% | 15.1 | 4,178 | 34,075 (1929) | Public Infrastructure | 2023 | 826 | |
| Finland | 5,926 | 3,270 | 55.18% | 57.06 | 929 | Nationalized | 2017 | 246 | ||
| Ukraine | 19,787 | 9,319 | 46.78% | 28.81 | 2,140 | Nationalized | 2019 | 804 | ||
| Romania | 20,077 | 6,600 | 30.42% | 22.13 | 1,823 | 23,955 | Nationalized | 2023 | 642 | |
| United States | 220,044 | 1,847 | 0.84% | 44.69 | 1,522 | 428,180 (1917) | Mostly Private | 2019 | 840 | |
| France | 27,483 | 16,067 | 58.46% | 22.78 | 2,374 | 63,000 (1923) | Nationalized | 2019 | 250 | |
| Japan | 27,311 | 20,534 | 75.19% | 16.1 | 5,451 | Both | 2015 | 392 | ||
| Mexico | 23,389 | 802.7 | 3.43% | 114.43 | 6,697 | 26,914 | Both | 2020 | 484 | |
| Brazil | 29,817 | 9,025 | 30.27% | 299.6 | 7,225 | Both | 2014 | 76 | ||
| Canada | 49,422 | 129 | 0.20% | 214.48 | 674 | 69,636 (1940) | Freight – Private | 2017 | 124 | |
| South Africa | 20,953 | 7,413 | 46.51% | 58.28 | 2,577 | Nationalized | 2017 | 710 | ||
| Germany | 40,625 | 22,500 | 55.38% | 9.26 | 2,145 | 61,498 (1910) | Nationalized | 2017 | 276 | |
| Poland | 19,576 | 12,236 | 62.51% | 16.28 | 2,001 | 27,000 (1954) | Nationalized | 2023 | 616 |
(Source: wikipedia.org)
Train Overview
- The global train industry has experienced significant growth in 2023 and 2024. According to recent Train Statistics, the high-speed rail sector continues to expand, driven by rising investments and the need for efficient transportation solutions. In 2023, the global high-speed rail market was valued at approximately $350 billion US dollars, and it is projected to reach around $380 billion US dollars by the end of 2024. This increase is primarily due to countries like China, Japan, and the United States investing heavily in rail infrastructure.
- China has emerged as the most significant player, accounting for about 45% of the global train market, especially in high-speed rail development. The “CRRC” company leads the market with substantial investments in domestic and international projects. The United States has also increased its focus on high-speed trains, with projects like the California High-Speed Rail, valued at $80.3 billion US dollars in 2023.
- Europe is also a key player, with the Trans-European Network being valued at $67 billion US dollars, representing a 5% increase from 2023. Japan, home to iconic trains like the Shinkansen, maintains a strong presence in the high-speed rail sector, contributing significantly to global Train Statistics.
- Investments in railway infrastructure are expected to grow by around 8% annually in 2024, particularly in Asia and Europe. These regions are focusing on environmentally friendly and efficient transportation solutions. Train Statistics suggest that the demand for high-speed trains will continue to rise, driven by passenger and freight transport needs. The train industry is on track to expand further as countries prioritize sustainable transport options.
Conclusion
The global train industry has grown and transformed significantly in recent years, with high-speed rail becoming increasingly prominent. Train Statistics show that China leads the market, accounting for nearly half the global share. At the same time, countries like Japan and the United States continue to invest heavily in rail infrastructure. The industry is valued at hundreds of billions of dollars, with projections indicating further growth.
As countries prioritize environmentally friendly transport options, the demand for high-speed trains will rise for passenger and freight transport.
Sources
FAQ.
The L0 series Maglev from Japan reached 603 km/h.
The United States, with 220,044 km of railway.
Union Pacific from the US, with a market value of $149.46 billion.
India, with 93.43% of its network electrified.
The UK’s High Speed 2 rail link is valued at $86 billion.
Approximately $350 billion as of 2023.

Saisuman is a skilled content writer with a passion for mobile technology, law, and science. She creates featured articles for websites and newsletters and conducts thorough research for medical professionals and researchers. Fluent in five languages, Saisuman's love for reading and languages sparked her writing career. She holds a Master's degree in Business Administration with a focus on Human Resources and has experience working in a Human Resources firm. Saisuman has also worked with a French international company. In her spare time, she enjoys traveling and singing classical songs. Now at Smartphone Thoughts, Saisuman specializes in reviewing smartphones and analyzing app statistics, making complex information easy to understand for readers.










