Semiconductor Supply Chain Statistics and Facts
Updated · Jul 02, 2025
Table of Contents
Introduction
Semiconductor Supply Chain Statistics: Semiconductors are materials with an electrical conductivity between the conductor and the insulator. Their behavior has made them a pivotal component of electronic devices, and this field has a considerable market size. To realize their significance on a global scale, it is essential to have a holistic understanding of Semiconductor Supply Chain Statistics. In this digital age, we will discuss the importance of semiconductor development.
Editor’s Choice
- The semiconductor industry is expected to recover in 2024 due to better inventory management and rising demand for advanced AI chips.
- The memory segment is predicted to play a significant role in this recovery.
- In 2023, the industry faced a downturn, leading to strategic plans from companies and governments to secure the industry’s future.
- Companies are addressing talent shortages to meet the growing demand for semiconductors as their applications expand.
- The semiconductor industry operates through three main business models: Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs), Fabless Design Companies, and Foundry Companies.
- IDMs, like Intel and Samsung, manage the entire semiconductor production process, from design to manufacturing.
- Fabless companies, such as Nvidia and Qualcomm, design semiconductors but outsource production to foundry companies.
- Foundry companies, led by TSMC, are responsible for manufacturing semiconductors.
- Semiconductor manufacturing is concentrated in regions like Taiwan and South Korea, leading to concerns over reliance on a few regions.
- Governments worldwide are investing in domestic semiconductor production to mitigate these concerns.
- In 2024, China announced a USD 47.5 billion investment fund to support chip manufacturing.
- The U.S. allocated USD 52 billion through the CHIPS Act to strengthen its semiconductor industry.
- Europe committed 43 billion euros through the European Chips Act to boost its semiconductor sector.
- Taiwan, South Korea, and Japan introduced tax incentives to promote collaboration and strengthen their semiconductor industries.
- The semiconductor industry has shown resilience, navigating challenges like geopolitical tensions and the growing AI chip market.
- The global semiconductor market is expected to grow to around USD 611 billion in 2024.
- Geopolitical issues, such as the U.S.-China tech conflict, will continue to impact the industry.
- The semiconductor sector is central to national security and economic policies, driving a race for investments.
- The U.S. CHIPS and Science Act aims to enhance supply chains, national security, and competitiveness, attracting investment in major semiconductor plants.
- Private investment in industrial facilities across all sectors is projected to increase by 85% in 2024 compared to 2019, though semiconductor production growth will likely lag until 2026.
- The U.S. CHIPS Act does not address challenges like vendor concentration, advanced packaging, and rising costs, potentially hindering supply chain development.
- The strategic rivalry between the U.S., EU, and China has disrupted supply chains and is expected to continue.
- Mainland China remains a major market for semiconductor suppliers, accounting for 30% of revenues for the 10 largest chip companies.
- Black-market sales, industrial espionage, and piracy could threaten international research and standards-setting.
- The semiconductor industry faces physical risks from war, natural disasters, and fires, which can disrupt production.
- New fabrication facilities must consider climate change factors, especially water availability.
- The COVID-19 pandemic exposed the vulnerability of semiconductor supply chains to demand-side shocks, particularly in the automotive sector.
History Of Semi-Conductor
- Thomas Johann Seebeck is credited with discovering the effect of semiconductors in 1821.
- In 1839, Micheal Faraday found a decrease in the resistance of silver sulphide on heating that led to the development of the concept of a semiconductor.
- Karl Ferdinand Braun is regarded as the first inventor of a semiconductor device, which was developed in 1874.
About Semiconductor Industry
- The semiconductor industry grew during the 1960s.
- As per semiconductor supply chain statistics, it is the electronic industry’s backbone.
![]()
(Reference: Statista.com)
- As per semiconductor supply chain statistics, Smartworks has gained significant revenue since 2020.
- As shown in the graph, smartphone revenue increased from $117 billion to $146 billion in 2025.
- Similarly, data centers have witnessed significant gains, with $136 billion in 2025 from $ 76 billion in 2020.
(Reference: Statista.com)
- Based on Semiconductor supply chain statistics, its revenue is predicted to be $687.38 billion by 2025.
- As of 2023, the revenue of the semiconductor market reaches $526.89 billion.
Semiconductor Market Revenue
(Reference: Statista.com)
- As per Semiconductor supply chain statistics, Intel is the clear winner in terms of revenue.
- In 2023, Intel's global revenue was $48.66 billion.
- Samsung Electronics has 2nd best revenue, with $39.91 billion in 2023.
![]()
(Reference: Statista.com)
- As per Semiconductor supply chain statistics, revenue market growth has fluctuated in the past 34 years.
- In 2024, the semiconductor market is expected to grow 16%.
- In 2023, semiconductor revenue decreased by 8.2%.
- It is predicted revenue is expected to reach a growth of 12.5%.
(Reference: Statista.com)
- The presence of a semiconductor foundry is a strong indicator of the industry's supply chain and market forces.
- Based on Semiconductor supply chain statistics, TSMC had the highest market revenue for semiconductor foundries, with 18,847 as of Q1 2024.
- Samsung is a distant second with 3,357 foundries in Q1 2024.
Semiconductor Revenue Region-wise
Referring to semiconductor supply chain statistics, having a holistic overview of revenue across different geographical spectrums is interesting.
Revenue worldwide
(Reference: Statista.com)
- The global revenue of the semiconductor market is projected to reach $607 billion by 2024.
- The integrated circuit market is the most dominant, with a projected market volume of $515 billion in 2024.
- There is a CAGR for 2024 – 2029, which is expected to be 10.06%, resulting in a market share of $980.08 billion by 2029.
Revenue in Asia
(Reference: Statista.com)
- As per semiconductor supply chain statistics, the market is expected to reach a revenue of $382.02 billion by the end of 2024.
- China is the highest revenue generation region, with $177.8 billion till June 2024.
Revenue in Europe
![]()
(Reference: Statista.com)
- As per semiconductor supply chain statistics, the market revenue is expected to reach $86.46 billion by 2029.
- Integrated circuits have a dominating position in the market, with revenue generation of $45.96 billion in 2024.
Revenue in Americas
(Reference: Statista.com)
- Based on Semiconductor supply chain statistics, the Semiconductor industry's revenue in the Americas in 2024 is expected to reach $163 billion.
- Regarding CAGR, revenue is expected to have an accumulated growth rate of 9.86% between 2024 and 2029.
Future Of The Semi-Conductor Industry
![]()
(Reference: semiconductors.org)
- Based on Semiconductor supply chain statistics, China showed the highest growth in FAB capacity, with 365% during 2012 -22.
- USA is expected to show a maximum growth rate in the period 2022 – 32 with 203%.
![]()
(Reference: semiconductors.org)
- Referring to semiconductor supply chain statistics, Taiwan is expected to remain the market leader in Semiconductor capex, with 31% in the period 2024 – 2032.
- The US is expected to be close second in semiconductor Capex with 28% from 2024 – 2032.
Semiconductor Supply Chain Challenges
- 40% of global CEOs have changed their supply chains to deal with geopolitical issues.
- Only 25% of CEOs in Japan's TMT industry have made similar changes.
- 32% of global CEOs plan to make their supply chains more resilient in the next six months.
- Only 13% of CEOs in Japan's TMT industry have the same plan for supply chain resiliency.
![]()
- Imbalance Between Supply and Demand: The demand for semiconductors, which are essential components in products like smartphones, computers, and automobiles, has exceeded supply due to factors like COVID-19 and natural disasters. These disruptions have led to significant shortages, impacting industries such as automotive and medical device manufacturing.
- Global Supply Chain Complexity: The semiconductor supply chain is highly intricate, involving numerous countries and companies. The process includes raw material supply, design, manufacturing, assembly, testing, and sales. The global nature of this supply chain often results in delays due to the need to transport materials and components across different countries, making it difficult for companies to respond quickly to changes in demand.
- Custom Specifications: Semiconductors are designed for various applications, leading to a wide range of product specifications. This diversity increases manufacturing and inventory management complexity. Companies must maintain a flexible supply chain to adapt to market changes while balancing the need for customized components.
- Lack of Incentives for Medical Semiconductors: Semiconductor manufacturers are less motivated to produce components for the medical sector, as these products often use older technology, are purchased in smaller volumes, and have stringent reliability requirements. This lack of incentive further exacerbates supply chain challenges for critical medical devices.
![]()
(Source: ey.com)
Resilience in the Semiconductor Supply Chain - BCG Report
Strengthening the Global Semiconductor Supply Chain
- The global semiconductor supply chain has traditionally relied on a highly integrated and geographically concentrated network. This setup has saved the industry between $45 billion and $125 billion annually, lowering semiconductor prices by 35% to 65%. These savings have driven the widespread adoption of technology products worldwide.
- However, this concentration has also introduced significant vulnerabilities. There are over 50 points in the supply chain where a single region controls more than 65% of the global market share. This dependency makes the entire industry susceptible to disruptions like pandemics, natural disasters, material shortages, or geopolitical conflicts.
- In response to these risks, governments and companies are taking steps to increase resilience in the semiconductor supply chain. The US CHIPS Act, passed in August 2022, includes $39 billion in grant incentives and a 25% investment tax credit to boost domestic semiconductor manufacturing.
- The European Union has also launched its European Chips Act. Mainland China continues to support its semiconductor industry with the third phase of its Integrated Circuit (IC) Industry Investment Fund. Similar initiatives are taking place in Taiwan, South Korea, Japan, India, and other regions.
- Private sector investment in semiconductor manufacturing is expected to surge, with projections of $2.3 trillion in wafer fabrication investments from 2024 to 2032. This marks a significant increase from the $720 billion invested in the previous decade.
- The US is set to benefit significantly from these investments, with its share of global capital expenditures expected to rise from 9% before the CHIPS Act to 28% by 2032. This shift will enhance the resilience of wafer fabrication, diversifying capacity beyond Taiwan and South Korea to include the US, Europe, and Japan.
- By 2032, the US is expected to increase its wafer fabrication capacity by 203%, raising its share of global capacity from 10% today to 14%. Without these actions, the US share would have fallen to 8% by 2032.
- In the assembly, test, and packaging (ATP) segment, Mainland China and Taiwan will continue to dominate, but countries in Southeast Asia, Latin America, and Eastern Europe are expected to expand their ATP activities with support from governments and foreign investors.
- The US is also working to build ATP capacity through the CHIPS Act and other government initiatives. This effort includes the development of advanced packaging technologies and innovations in chiplets, which are driving investments in the US and Europe.
- Emerging markets are actively pursuing strategies to attract ATP investment, contributing to a more resilient and diversified semiconductor supply chain globally.
The Expansion of Government Incentives
- Semiconductor companies consider many factors when deciding where to invest, such as business conditions, supplier networks, site availability, infrastructure, and workforce.
- Government policies play a critical role in these decisions. Effective incentive programs, supportive regulations, and talent development initiatives show a government’s commitment to the industry's success.
- Strong policies can reduce costs and improve the efficiency of building and running semiconductor facilities.
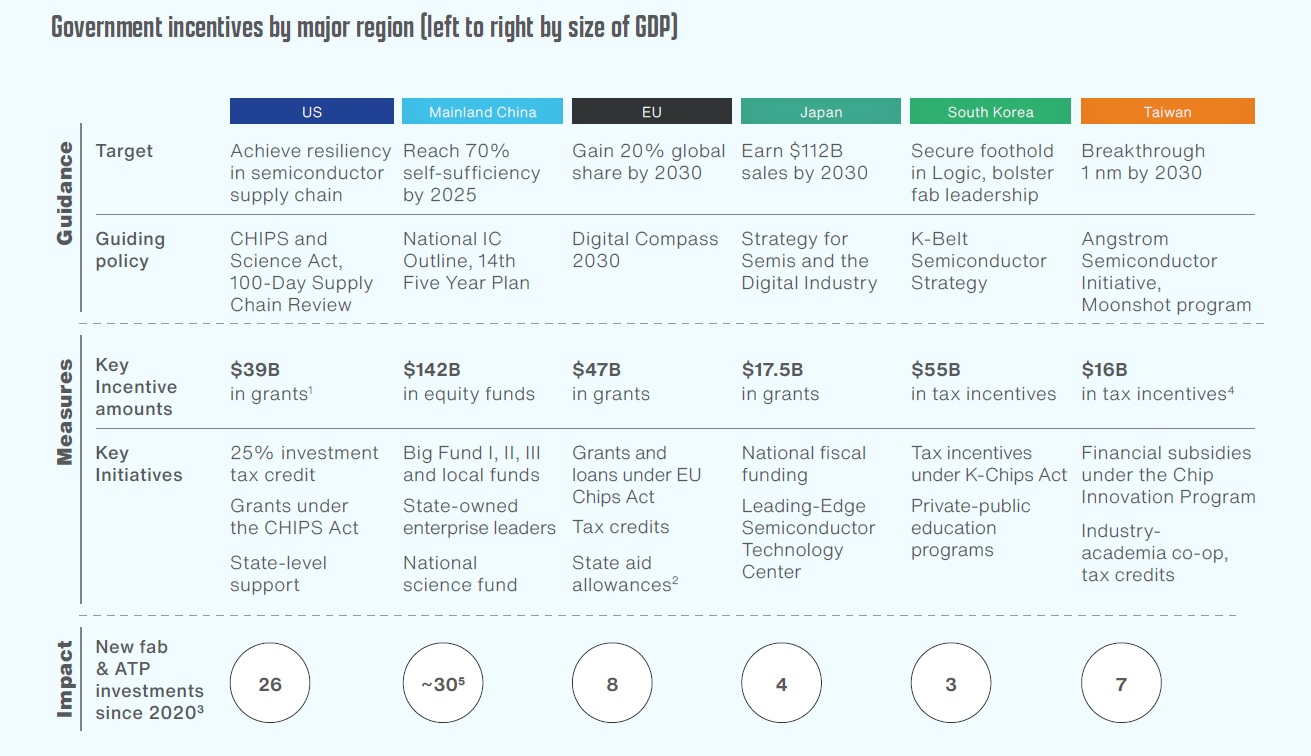
(Source: Gartner; SIA; Press releases; Company disclosures; Government websites; BCG analysis)
- Since 2021, global governments have significantly increased support for the semiconductor industry.
- The U.S. introduced the CHIPS Act, providing direct grants and a 25% tax credit for semiconductor manufacturing.
- The CHIPS Act allocates $11 billion of its $52 billion budget to bolster U.S. leadership in semiconductor research and development (R&D).
- The EU and Japan have launched substantial grant funds and tax incentives, distributed based on national priorities and specific projects.
- South Korea and Taiwan offer extensive tax incentives and R&D support, including the Taiwan Chip Innovation Program and South Korea’s K-CHIPS Act.
- Governments are also using indirect methods, such as infrastructure support, affordable land, and streamlined approval processes to attract investment.
- Mainland China has provided significant support through equity infusions and funds that combine government and private capital.
- Additional measures in China include acquiring overseas talent, creating domestic standards, and promoting state-owned enterprises, which favor locally produced chips.
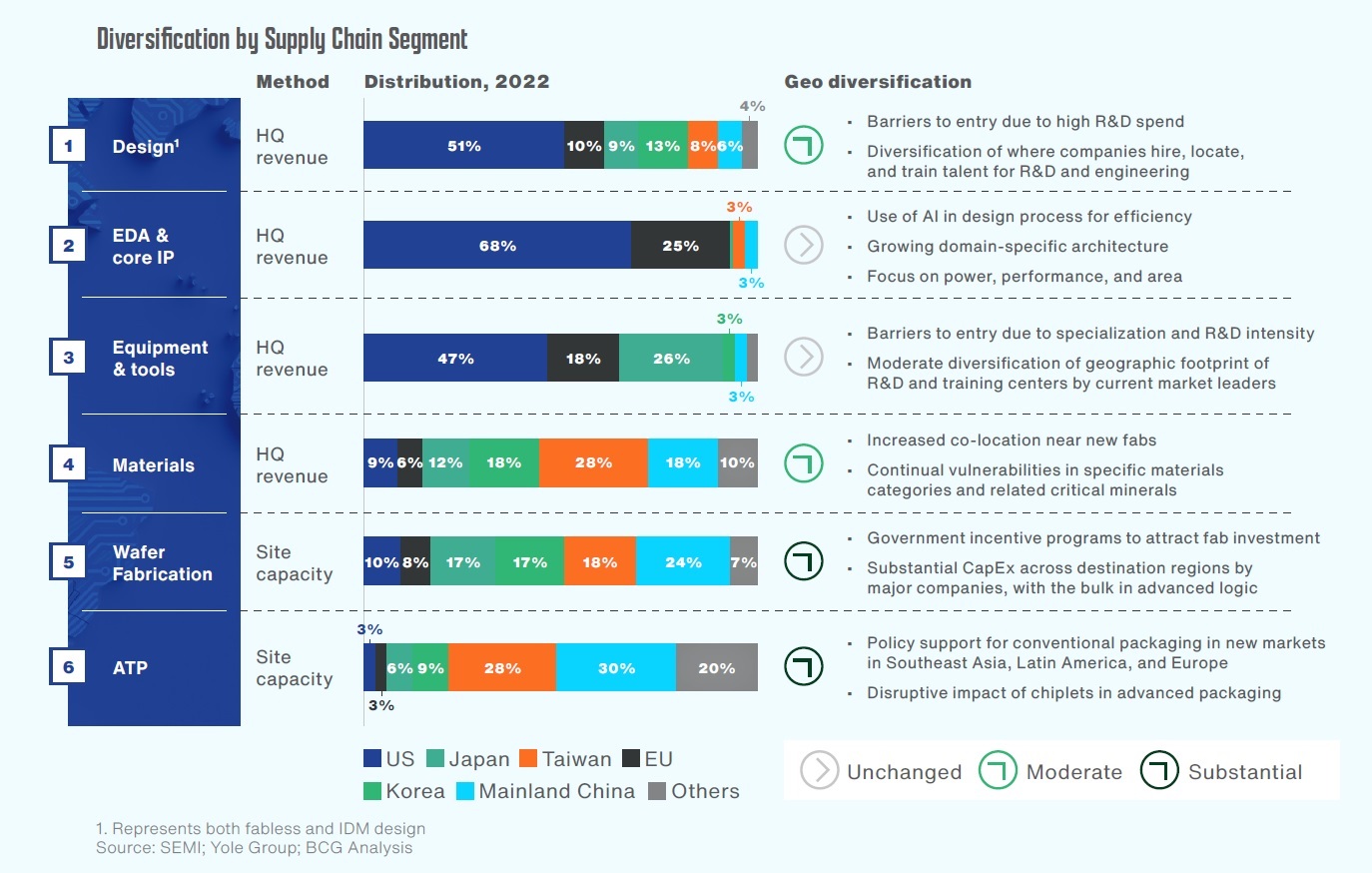
Reshaping the Global Semiconductor Supply Chain
- The global semiconductor supply chain is highly specialized, with different regions excelling in various segments.
- U.S. companies dominate in design, core intellectual property (IP), and electronic design automation (EDA).
- The United States, European Union, and Japan lead in semiconductor equipment production.
![]()
- Mainland China, Japan, Taiwan, and South Korea are leaders in supplying materials.
- South Korea and Taiwan are global leaders in advanced chip fabrication, particularly for sub-10 nanometer technologies.
- The assembly, testing, and packaging (ATP) segment is primarily concentrated in Mainland China and Taiwan.
- The specialization by region has benefited from a globally integrated supply chain, allowing each region to access global markets.
- However, this geographic concentration has also created vulnerabilities, prompting a need for diversification.
- Significant geographic diversification is expected, particularly in wafer fabrication, with an emphasis on advanced logic chips.
- There will be efforts to diversify ATP activities outside of Mainland China and Taiwan, targeting new markets. However, ATP is unlikely to move significantly to the United States due to cost pressures.
- Some diversification is also expected in design and materials, driven by global talent sourcing and following new fab investments.
- Diversification in equipment, EDA, and core IP will be challenging due to their high specialization and the lack of necessity for proximity to fab sites.
- Wafer fabrication will see substantial investment, as it influences the entire supply chain.
- Investment in wafer fabrication is projected to reach $2.3 trillion between 2024 and 2032, a significant increase from $720 billion invested between 2013 and 2022.
- Over 100 major semiconductor manufacturing projects have been announced since the last report, spread globally and across new locations in key regions.
- In Asia, investments are accelerating. Taiwan plans to build seven new fabs. TSMC is collaborating with Sony, DENSO, and Toyota in Japan for advanced manufacturing capabilities. South Korea plans a $471 billion investment through 2047 for a mega chip cluster involving Samsung and SK Hynix. Mainland China is investing in new fabs in Shenzhen, Tianjin, and Shanghai.
- The United States has seen 80 new semiconductor manufacturing projects between 2020 and 2023, expected to create 50,000 jobs. These investments are spread across traditional hubs like Texas, Arizona, New York, and California, with new expansions in regions like New Albany, Ohio.
- Europe is experiencing substantial growth in semiconductor capacity, with major investments in Germany, France, and Poland. Intel and TSMC are key players in these developments, especially in Germany and France.
- Significant investments are expected across regions until 2032, driving the diversification of the semiconductor supply chain globally.
Conclusion
Referring to semiconductor supply chain statistics, it can be easily said that semiconductors are expected to remain in significant growth. There are a variety of challenges caused by disruption and geopolitical tensions. This industry is expected to be bolstered by the rise of demand for emerging technologies such as AI, 5G and IoT.
Globally, Asia remains the most domain region of semiconductor supply chain. With a projected revenue of $687.38 billion in 2025 and increasing investment in the R&D semiconductor industry, it is poised for a bright future.
FAQ.
Thomas Jane Seebeck discovered the electrical properties of semiconductors in 1821.
Based on semiconductor supply chain statistics, revenue in America is expected to be $163 billion in 2024.
Approximately $80 billion is the revenue spent in R&D for semiconductor revenue in 2023.

Joseph D'Souza founded ElectroIQ in 2010 as a personal project to share his insights and experiences with tech gadgets. Over time, it has grown into a well-regarded tech blog, known for its in-depth technology trends, smartphone reviews and app-related statistics.










